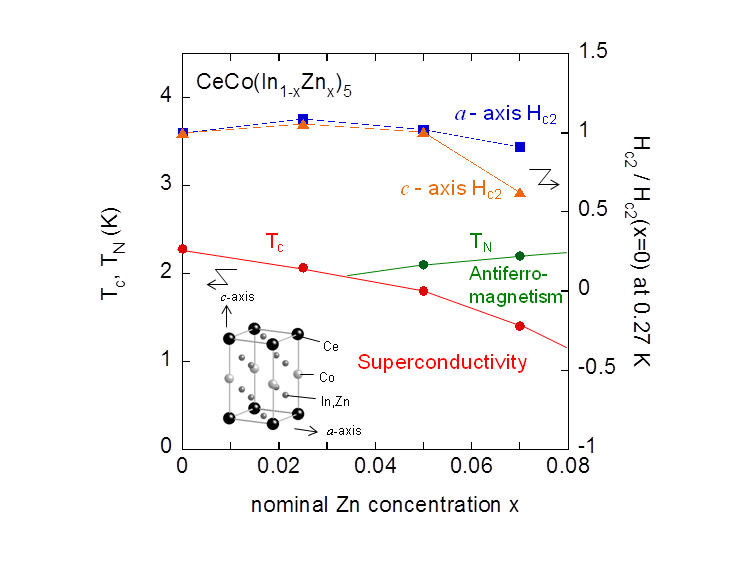
In general, stability of superconducting phase against both temperature and magnetic field is simply dominated by a single order parameter of superconductivity. The Pauli-limited superconductivity in CeCo(In1-xZnx)5, however, does not seem to meet such an expectation. We reveal that the substitution of Zn for In up to x~0.05 yields little change of superconducting upper critical field, though it reduces superconducting transition temperature to 80% of that for x=0. The key to resolve this unusual feature is a development of antiferromagnetic correlation in these alloys; the antiferromagnetic correlation enhanced by doping Zn relaxes the Pauli paramagnetic suppression of the superconducting upper critical field, and then, balance between this effect and suppression of SC condensation energy leads to the robust x dependence of the superconducting upper critical field.
The article regarding this work:
M. Yokoyama, H. Mashiko, R. Otaka, Y. Sakon, K. Fujimura, K. Tenya, A. Kondo, K. Kindo, Y. Ikeda, H. Yoshizawa, Y. Shimizu, Y. Kono, and T. Sakakibara:
"Pauli-limited superconductivity and antiferromagnetism in the heavy-fermion compound CeCo(In1-xZnx)5",
Physical Review B 92, 184509-1-9 (2015).
link to this paper
